One of the (many) fascinating things about this latest global financial crisis is that there’s no single catalyst. Unlike 2008 when the carnage could be traced back to US subprime housing, or 2000 when tech stocks crashed and pulled down everything else, this time around a whole bunch of seemingly-unrelated things are unraveling all at once.
China’s malinvestment binge is crashing global commodities, an overvalued dollar is crushing emerging markets (most recently forcing China to devalue), the pan-Islamic war has suddenly gone from simmer to boil, grossly-overvalued equities pretty much everywhere are getting a long-overdue correction, and developed-world political systems are being upended as voters lose faith in mainstream parties to deal with inequality, corporate power, entitlements, immigration, really pretty much everything. For one amusing/amazing example of the latter problem, consider Germany’s response to the mobs of men that suddenly materialized and began molesting women: Cologne mayor slammed after telling German women to keep would-be rapists at arm’s length.
Why do causes matter at times like this? Because where previous crises were “solved” with a relatively simple dose of hyper-easy money, it’s not clear that today’s diverse mix of emerging threats can be addressed in the same way. Interest rates, for instance, were high by current standards at the beginning of past crises, which gave central banks plenty of leeway to comfort the afflicted with big rate cut announcements. Today rates are near zero in most places and negative in many. Cutting from here would be an experiment to put it mildly, with myriad possible unintended consequences including a flight to cash that empties banks of deposits and a destabilizing spike in wealth inequality as negative interest rates support asset prices for the already-rich while driving down incomes for savers and retirees.
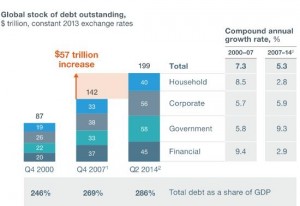
And with debt now $57 trillion higher worldwide than in 2008, it’s not at all clear that another borrowing binge will be greeted with enthusiasm by the world’s bond markets, currency traders or entrepreneurs. Here’s that now-famous chart from McKinsey:
Easier money will have no effect on the supply/demand imbalance in the oil market, which is still growing. The likely result: Sharply lower prices in the year ahead, leading to a wave of defaults for trillions of dollars of energy-related junk bonds and derivatives.
As for stock prices, in the previous two crises equities plunged almost overnight to levels that made buying reasonable for the remaining smart money. Today, virtually every major equity index remains high by historical standards, so the necessary crash is still to come — and will add to global turmoil as it unfolds.
The upshot? It really is different this time, in a very bad way. And this fact is just now dawning on millions of leveraged speculators, mutual fund and pension fund managers, individual investors and central bank managers. Right this minute virtually all of them are staring at screens, scrolling over to the sell button, hesitating, pulling up Bloomberg screens showing how much they’ve lost in the past few days, calling analysts who last year convinced them to load up on Apple and Facebook, getting no answer, going back to Bloomberg and then fondling the sell button some more. Think of it as financial collapse OCD.
What happens next? At some point — today or next week or next month, but probably pretty soon — the dam will break. Everyone will hit “sell” at the same time and find out that those liquid markets they’d come to see as normal have disappeared and yesterday’s prices are meaningless fantasy. The exits will slam shut and — as in China last night where the markets closed a quarter-hour into the trading session — the whole world will be stuck with the positions they created back when markets were liquid and central banks were omnipotent and government bonds were risk-free and Amazon was going to $2,000.
And one thought will appear in all those minds: Why didn’t I load up on gold when I had the chance?





