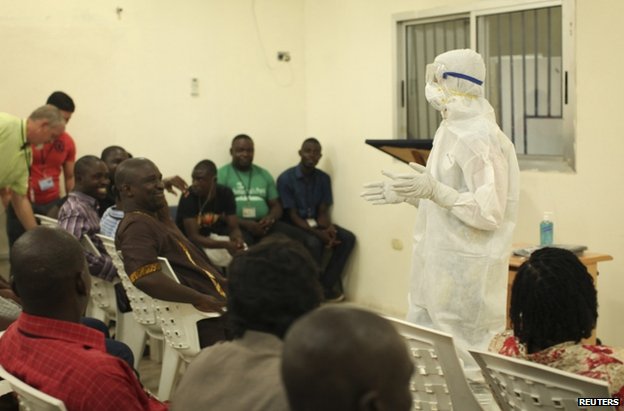
The WHO meeting on Ebola Epidemic has reaffirmed the need for high national leadership by heads of states and government to facilitate an inter-sectoral interventions and coordination required to cope with the disease.
The WHO meeting on Ebola Epidemic has reaffirmed the need for high national leadership by heads of states and government to facilitate an inter-sectoral interventions and coordination required to cope with the disease.
A communiqué read at the end of the EVD meeting also called on the Africa Union and ECOWAS to provide political and diplomatic support and recommended that the forthcoming ECOWAS Heads of States summit in Accra to address the issue of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreak.
The two- day EVD meeting was to obtain consensus from member states and partners represented on the optimal way of interrupting the ongoing Ebola virus transmission in West Africa to reduce the human, social and economic impact of the EVD outbreak in West Africa for the current and future outbreaks.
Governments were tasked to mobilise relevant sectors, community religious leaders to work together in improving awareness, psycho-social support and understanding of the disease situation by communities in order to achieve a more effective response.
They were required to convene inter-sectoral meeting involving key stakeholders including minster, community members, and technical coordinating committee members to map up a road map for immediate implementation of the strategy adopted at the meeting and identify and commit additional domestic financial resources to support the outbreak response.
Governments were also asked to organise cross boarder consultations to facilitate exchange of information and agree on joint collaborative activities as well as strengthen surveillance , case finding , reporting and contact tracing and to share information on EVD with WHO in a timely manner.
The communiqué urged government to pay their contributions to the Africa Public Health Emergency Fund (APHEF) to support response to outbreaks and other public health emergencies and improve information and communication to communities on matters related to the disease, respecting the different cultural context to enhance awareness creation and favourable behaviour needed to improve community participation in prevention, curative and health promotion interventions.
Development partners were to continue in the response activities in line with the identified country priority areas, provide technical and financial assistance , ensure a coordinated approach in resource mobilisation and allocation and continue to work with WHO in a coordinated manner to ensure a more effective response at all levels.
WHO were tasked to provide leadership in coordinating the international partners at global, regional and country level in support of national plans, urgently establish a sub-regional control centre in Guinea to act as a coordinating platform to consolidate and harmonise technical support to West African countries by all major partners and assist in resource mobilisation
WHO was also entreated mobilise and deploy the needed WHO staff, and other expert, consultants, institutions and networks especially through networks to support the the onongoing EVD outbreaks to stakeholders.
They are to develop and disseminate information, education and communication materials for the public and additional training materials for health professionals and risk assessment on the EVD, facilitate cross border inter-country collaboration with countries and lead an international effort to identify, and prioritise key gaps and promote research on the EVD and other hemorrhagic fevers